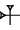 , 2 (ban2):
, 2 (ban2):  , 3 (ban2):
, 3 (ban2):  , 4 (ban2):
, 4 (ban2): 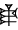 , 5 (ban2):
, 5 (ban2): 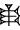

Return to Numbers & Metrology in the 2nd millennium
Sources: the diagrams below represent data provided by metrological lists and tables from Nippur
scribal schools. These sources are available on CDLI (here).
Scope: Similar metrology is attested in other Old Babylonian scribal schools. The metrology taught in scribal schools was adopted in a large part of Mesopotamia. However, some minor variants may be observed in some administrative or economic archives from Southern Mesopotamia.
Bibliography:
| še |  | ca. 0.04 g |
| ↓ × 180 | ||
| gin2 |  | ca. 8 g |
| ↓ × 60 | ||
| ma-na | 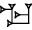 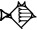 | ca. 500 g |
| ↓ × 60 | ||
| gun2 | 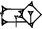 | ca. 30 kg |
| sar |  | ca. 36 m2 |
| ↓ × 100 | ||
| GAN23) | 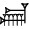 | ca. 3600 m2 |
System G, used before the sign GAN2
 | × 10 ← |  | × 6 ← | 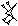 | × 10 ← | 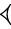 | × 3 ← |  | × 6 ← |  | × 2 ← | 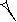 |
| šar’u | šar2 | bur’u | bur3 | eše3 | iku | ubu | ||||||
| 10 800 iku | 1 080 iku | 180 iku | 18 iku | 6 iku | 1 iku | ½ iku |
Examples:

 1(iku) GAN2 represents ca. 3600 m2
1(iku) GAN2 represents ca. 3600 m2
![]()
 2(eše3) GAN2 represents ca. 2×6×3600 m2, that is, 43 200 m2
2(eše3) GAN2 represents ca. 2×6×3600 m2, that is, 43 200 m2
| šu-si |  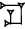 | ca. 16 mm |
| ↓ × 30 | ||
| kuš3 | 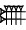 | ca. 50 cm |
| ↓ × 12 | ||
| ninda | 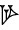 | ca. 6 m |
| ↓ × 60 | ||
| UŠ |  | ca. 360 m |
| ↓ × 30 | ||
| danna | 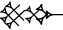 | ca. 10,5 km |
Note: in mathematical texts, the unit gin2 is also used for sub-dividing the surface unit sar into 60 parts, and the unit še is also used in capacity and surface systems for sub-dividing the unit gin2 into 180 parts. In other words, if we consider all of the OB mathematical texts, the sequence ←×60− gin2←×180−še can be grafted in capacity and surface systems.
Bridge between length and surface units: 1 ninda × 1 ninda = 1 sar
Bridge between surface and volume units: 1 volume-unit = 1 surface-unit × 1 kuš3 (example: 1 sar-volume = 1 sar-surface × 1 kuš3).
Bridge between volume and capacity units: 1 sar-volume is equivalent to 60 gur (ca. 18 m3 or 18 000 liters).
 | × 10 ← |  | × 6 ← |  | × 10 ← | 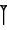 | × 6 ← | 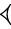 | × 10 ← | 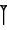 |
| šar’u | šar2 | geš’u | geš2 | u | diš | |||||
| 36 000 | 3 600 | 600 | 60 | 10 | 1 |
Some metrological lists or tables provide very large (and unrealistic) numbers:
A school tablet from Nippur CBS 11319 +) contains on the obverse the unique known text which displays the entire System S in a systematic way (see copy and transliteration in Proust 2008, in Proceedings of the 51st Rencontre Assyriologique Internationale, Biggs et al. ed., SAOC 62, p. 151-152).
The highest units of capacity (gur) and weight (gun2) are counted with a variant of System S, where the number 1 is represented by the sign aš ![]() (and not the sign diš
(and not the sign diš ![]() as in the System S used for discrete item).
as in the System S used for discrete item).
The other measuring units (sila3, gin2, še, sar, danna, UŠ, ninda, kuš and šu-si) are counted with ![]() (1) and
(1) and ![]() (10) repeated as many times as necessary.
(10) repeated as many times as necessary.
| 1/6 | 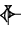 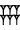 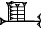 (igi-6-gal2) (igi-6-gal2) |
| 1/3 |  |
| 1/2 |  |
| 2/3 | 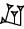 |
| 5/6 | 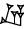 |
Page prepared by CP
(digital version prepared by BG)